Congratulations! You’ve taken the first step towards your independence from eyeglasses or contact lenses.
Glasses or contact lenses are designed to compensate for the eye's imperfections. They however address the symptoms of the problem, not the problem itself. After the introduction of laser vision correction in the late1980s, patients could get rid of glasses or contact lenses as instead of treating the symptoms of poor vision, the laser aimed to permanently correct an incorrectly-curved cornea to restore vision. In LASIK surgery, precise and controlled removal of corneal tissue by a special laser reshapes the cornea changing its focusing power. This approach changed the landscape of vision correction dramatically and since then, more than 20-million eyes worldwide have been corrected by laser.
Laser Vision correction or LASIK is now the most popular procedure worldwide to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness and astigmatism. Its popularity is based on the high rate of patient satisfaction, excellent visual results, quick recovery and the very few side effects and complications.
Not all patients are, however, suitable candidates for LASIK. The good news is that, apart from the very popular Lasik treatment, several other options are also available, including the alternative techniques of Photo Refractive Keratectomy (PRK), implantation of a Phakic intra-ocular lens and a clear lens replacement
 |
 |
 |
 |
Normal |
Myopia |
Hyperopia |
Astigmatism |
There are three primary types of refractive errors: Myopia, Hyperopia and Astigmatism.
Persons with myopia, or nearsightedness, have more difficulty seeing distant objects as clearly as near objects.
Persons with hyperopia, or farsightedness, have more difficulty seeing near objects as clearly as distant objects.
Astigmatism is a distortion of the image on the retina caused by irregularities in the cornea or lens of the eye. Combinations of myopia and astigmatism or hyperopia and astigmatism are common.
| • Conventional LASIK corrects your vision based on your prescription for contacts or glasses. Your level of vision correction is determined using the familiar "which is better, this or that?" vision test. |
| • Wavefront optimized LASIK is a newer technology that corrects refractive errors while accounting for both the natural curvature of the eye and the unique characteristics of each individual’s eye. Because this type of LASIK follows the shape of the eye more closely, it has less risk of inducing subtle vision problems, called higher order aberrations, than conventional LASIK. |
| • Custom LASIK, creates a personalized map of existing higher order aberrations to correct refractive error and these more subtle vision problems. Higher order aberrations may include subtle blurring, less clear visual contrast and even mild glare, halos or starbursts around lights at night. |
• A highly-accurate measurement device, the Zeiss Atlas Topography System (below left), measures the characteristics and deviations of the cornea to within sub-micron accuracy. Complex software algorithms are then applied to these measurements by the patented CRS-Master software (below middle) to calculate the exact amount of corneal tissue to be removed at every point on the corneal curvature to optimise the visual outcome. It is then passed to our Carl Zeiss MEL-80 excimer laser (below right) which is one of the most efficient excimer lasers which enables extremely safe and precise correction. 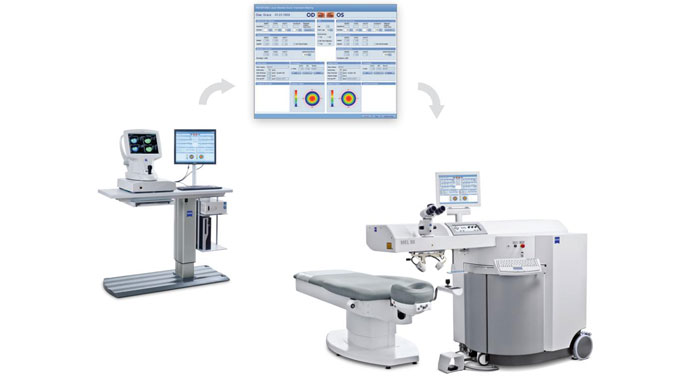 |
| • The laser is guided by an active eye tracking mechanism that samples the position of the eye 1050 times per second. So, if your eye should accidentally wander during the treatment, the eye tracking mechanism detects the movement and redirects the laser beam to the correct location on the surface of the cornea. |
• Since the laser fires at 250 pulses per second, the eye tracker samples the position of the eye 4 times faster than the laser, making it the only laser on the market to track each pulse individually. Many other lasers will only track between 30% and 50% of the pulses applied.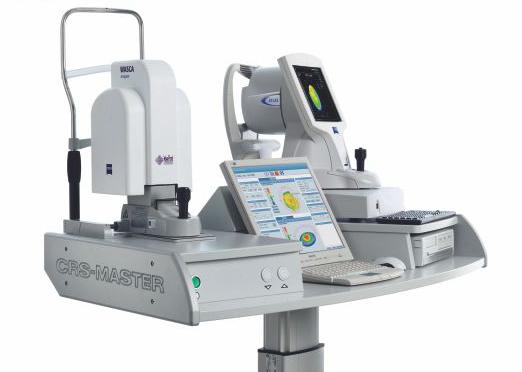 |
| 1. A thin flap is created in the surface layer of the cornea and folded to one side. |
| 2. The exposed area is then reshaped by very accurately-targeted excimer laser pulses. Complex mathematical algorithms guide the laser to remove microscopic amounts of corneal tissue at pre-determined positions on the cornea to correct its overall curvature. Special eye trackers in the system reassuringly will compensate for involuntary eye movements. |
| 3. The flap is then replaced into its original position and re-attaches itself to the cornea over time. |
The whole LASIK procedure is completed in about 10 minutes
Since the curvature of the cornea is permanently reshaped, it corrects the refractive error.
| • Are 18 years of age and above(there is no upper age restriction) |
| • Are not pregnant/breast feeding |
| • Are free of any chronic eye disease |
| • Possess stable refractive error |
Please check with your doctor on the importance of possessing realistic expectations and understanding of the potential risks and side effects that may occur.
To find out if you are a good candidate for LASIK, please contact Aggarwal EYE Hospital today.
| • A full review of the overall health of your eyes. |
| • The measurement of corneal thickness and shape, including corneal topography. |
| • A complete review of your glasses and contact lens history. |
| • The measurement of your prescription and refractive error in each eye. |
| • Dilation of the eyes to check the health of the retina and optic nerve. It also helps to determine the actual absolute power of the eye. |
| • Custom measurement for higher order aberrations. |
| • Dry eye test. |
| • A personal consultation. |
During this evaluation, the patient’s visual system is examined with particular attention to issues which could affect a satisfactory outcome or which could increase the patient’s risk to encounter a side effect or complication from the procedure.
In addition, this is the time for the patient to have all questions and concerns addressed.
This process is crucial in determining your suitability and safety for LASIK.
| • Contact lens wearers: You’ll need to remove your contacts for a period of time prior to the laser vision correction treatment so that your cornea can return to its normal, natural shape. |
| • Not leaving your contact lenses out long enough for your cornea to assume its natural shape before surgery can have negative consequences which include inaccurate measurements and a poor surgical plan, resulting in poor vision after surgery. If you wear: |
| • soft contact lenses, you should stop wearing them for 2 weeks before your initial evaluation. |
| • toric soft lenses or rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses, you should stop wearing them for at least 3 weeks before your initial evaluation. |
During the first week your vision will recover rapidly and after 4 weeks your eyes will be close to their optimal visual acuity. It may, however, take 3 months before vision stabilises completely, depending on the initial refractive error. If you fall in the presbyopic age (40 to 45 years and older), you will require reading glasses shortly after surgery.
Some of the restrictions after laser treatment include:| • No mascara or eyeliner for two weeks . |
| • Extra care should be exercised when bathing and washing hair to avoid unnecessary soap and water in the eye for two weeks. |
| • No swimming for six weeks. |
| • No rubbing of the eyes (to ensure that the lamellar flap is not disturbed and stays in place). |
You may drive as soon as you feel comfortable to do so. Your night driving vision may take longer to recover than your daytime vision, due to a temporary halo and starburst effect, which you may perceive around lights.
Follow up visits will be scheduled at day one, week one, month 1 and month 3 after the procedure to ensure that your vision and the physical condition of your eyes are recovering as they should.
WHAT CAN YOU EXPECT YOUR EARLY VISION TO BE?
You may typically experience small fluctuations and blurriness in your vision for the first week to a few months as your eyes continue to heal. The time it takes you to heal will depend on the level of nearsightedness, farsightedness and/or astigmatism that was treated. It is common, however, for most patients to see enough to resume their regular activities very quickly.
| • Your eyes are thoroughly examined beforehand to identify any contra-indications. |
| • The deviations on each eye are accurately measured. |
| • The correct laser procedure is chosen and performed by a skilled and experienced ophthalmologist under sterile conditions. |
| • You co-operate during the procedure. |
| • You faithfully use the prescribed medication afterwards. |
| • You take good care of your eyes, especially during the first two weeks after the procedure. |
Q: How Long Does the Procedure Typically Take?
A: The entire surgical procedure takes only 10 minutes or less per eye. The actual amount of time the laser is active on the eye is only one minute or less.
Q: Is the effect of LASIK vision correction permanent?
A: Yes. Following an initial healing period of few months, the effect of the treatment is lifelong.
Q: How soon does your vision change?
A: Most patients will already notice much improved vision without glasses immediately after the procedure. However, the most dramatic improvement is noticed after resting the eye overnight. Most LASIK patients see well the day after their procedure and may resume most of their normal daily activities soon after. But for about two to three weeks your vision may fluctuate.
Q: How soon can I resume my normal activities?
A: You can resume your normal activities like reading, computer work, watching television, etc. after the day 1 of treatment. However, continue to protect your eyes from anything that might get into them. Full visual recovery takes approx. 2-3 weeks. Most people will be able to return to normal work on the second day after surgery. Occasionally people may need a longer period off work (fewer than 5%).
Q: Can a laser treatment cause cataract, glaucoma or other eye problems?
A: Laser treatments will not cause any of these eye problems, nor will it treat them.
PRK is the acronym for Photo Refractive Keratectomy. It is the first laser vision treatment developed in 1988 to permanently correct vision and today remains the preferred treatment option for patients whose corneas are too thin for Lasik.
PRK differs from other laser treatments in that the treatment is applied directly on the surface of the cornea. The permanently reshaped cornea corrects the refractive error.Although the initial healing phase is significantly longer, the visual end-result is similar to Lasik.
The first Photo Refractive Keratectomy (PRK) procedure was performed in 1988 and has proven itself to be safe, highly accurate and has yielded excellent results. In certain cases, like marginally thin corneas, PRK is still the preferred method of treatment.
Click on this picture to see an animated illustration of PRK.
Procedure: The epithelial layer on the surface of the cornea is removed whereafter the exposed surface of the cornea is reshaped with an excimer laser. A 'bandage' contact lens is placed on the cornea to promote healing. After about 72 hours, when the epithelium has healed, the contact lens is removed.
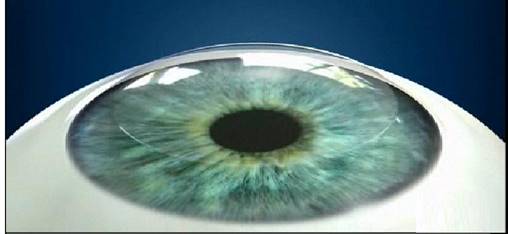
Since only the epithelial layer on the surface of the cornea is removed, there is minimal structural impact on the cornea. Note the 'bandage' contact lens on the cornea.
| • Since PRK is a surface treatment, the biomechanical integrity of the cornea remains largely intact. |
| • Due to the simplicity of the technique, PRK is still the most economical option for corneal laser vision correction. |
| • The recovery period for stable vision is longer compared to other corneal laser techniques, with some discomfort during the first 72 hours. |
| • Because of the longer recovery time, only one eye is treated at a time, as you will need full use of your other eye while the treated eye heals. |
| • Vision may fluctuate for up to 3 months, since the healing process of the cornea takes some time. Moreover, the epithelium has to be polished by the continuous blinking action of the eyelids. However, after two weeks most of the healing has occurred and you can expect relatively stable vision thereafter. |
| • If a further correction is required, it should only be done after 3 months when vision has fully stabilised. |
| • When the procedure was first introduced in the late 1980s, there was a small risk of scar formation on the cornea if the post-operative instructions were not adhered to. However, due to improved surgical techniques, good aftercare, the use of prescribed eye drops and protection of the eye against harmful UV rays, this risk today is extremely small. |
Image formation within the eye mainly occurs by means of the cornea and the crystalline lens. Here, the refractive power of the eye is modified by implanting extra lens power into the eye. ICLs are specialized lenses made of plastic or silicone material, which are implanted into the eye through a small incision without removing the eye's natural lens
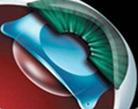 The most popular and successful phakic lens currently available is the STAAR ICL™. Various clinical criteria provide guidelines on the selection of the proper lens for implantation.
The most popular and successful phakic lens currently available is the STAAR ICL™. Various clinical criteria provide guidelines on the selection of the proper lens for implantation.
A phakic intraocular lens is indicated for those cases where the refractive error is beyond the scope of correction by other modalities.
| • Short-sightedness (myopia): up to -25.0 diopter |
| • Far-sightedness (hyperopia): up to +15.0 diopter |
| • astigmatism: up to -7.5 diopter |
| • Combinations of astigmatism and hyperopia/myopia |
These refractive errors fall outside the range of laser or other refractive surgeries, as this will result in extremely poor quality of vision.
ADVANTAGES OF PHAKIC LENSES| • In contrast to other refractive techniques, very high degrees of astigmatism, near sightedness and farsightedness can be corrected. |
| • Suitable for different patients: Since the ICL treatment is completely safe even if you have thin corneas, dry eyes, or large pupils (as it does not involve removing tissue from the cornea), it may be suitable for candidates who are otherwise unfit for Laser vision correction. |
| • The procedure is fully reversible. The lens may be removed at a later stage, replaced or changed if the prescription changes. |
| • The cornea, which is the most important refractive component of the eye, remains intact. There are consequently no permanent changes to the actual structure of the eye. |
| • In the past there was a risk that a cataract could form. New techniques reduced the risk substantially but, should it nevertheless occur, it can be treated. |
| • As this is an intraocular procedure, there is a small risk of infection. We do, therefore, take extensive precautions against infection by doing the operation in a sterile environment, and provide detailed instructions for after-care to the patient. |
| • Due to the mechanics of fluid distribution within the eye, the pressure within the eye may rise shortly after the procedure if the lens is not in perfect position. For this reason, we always keep our patients for an hour or two for observation after the procedure, so that we may react promptly upon any sign of pressure increase. During this time, you may relax in our company, and enjoy a cup of tea and sandwiches, or just doze off after the anaesthetic. |
| • Phakic lenses are relatively expensive, since these lenses are made to the patient’s prescription. |
With refractive lens exchange (RLE) — also called Clear Lens Extraction or CLE — an artificial lens is used to replace your eye's natural lens in order to improve vision. The procedure is performed much like cataract surgery. This option is also available in selected cases of refractive correction, namely patients with extreme pathological refractive errors.
As is an option in cataract surgery, RLE may employ multifocal or accommodative intraocular lenses (IOLs). These lenses allow the ability to focus at all distances.
The principal disadvantage of replacing the natural lens, is the resultant loss of natural accommodation (the ability to adjust focus). It is therefore mainly employed in cases where patients have already lost their accommodation due to the natural ageing process, namely the presbyopic group of patients older than 40 years.
© Aggarwal Eye Hospital |
Site designed by Rainbow Web |